
Leaning About Datacenter Proxies: A Comprehensive Guide
What is a Datacenter Proxy?
A datacenter proxy is an intermediary server that offers IP addresses not associated with Internet Service Providers (ISPs) or end-users but rather with large-scale data centers.
These proxies are created and managed by companies that own vast amounts of IP addresses housed in robust data centers.
Using a datacenter proxy allows users to mask their original IP address, making it appear as if their internet traffic originates from the proxy server.
This is particularly useful for tasks requiring anonymity, high-speed data retrieval, and large-scale web scraping.
Litport is one such provider offering reliable proxy services.
How Are Datacenter Proxy IP Addresses Created?
Datacenter proxy IP addresses are generated by leasing or purchasing IP ranges from organizations that own large blocks of IP addresses. These addresses are then assigned to servers within a data center.
The key steps involved include:
- Acquisition of IP Ranges: Providers lease or buy IP addresses from larger entities.
- Assignment to Servers: These IPs are allocated to servers in a data center.
- Configuration: Proxies are configured to manage traffic, ensuring they can handle multiple requests without compromising speed or security.
Table: Creation Process of Datacenter Proxy IP Addresses

What Are Datacenter Proxies Used For?
Scraping SERP Data (SEO)
Datacenter proxies are vital for scraping Search Engine Result Pages (SERPs) for SEO purposes.
They allow marketers to gather large volumes of data on keyword rankings, competitor analysis, and search trends without being blocked by search engines.
Analyzing Websites in Bulk
Web analysts often need to gather data from numerous websites simultaneously. Datacenter proxies enable this by distributing requests across multiple IPs, avoiding rate limits, and reducing the risk of IP bans.
Market Data Research
Businesses rely on datacenter proxies for market research, including price comparisons, product availability checks, and monitoring market trends.
This is essential for staying competitive and making informed business decisions.
Table: Uses of Datacenter Proxies

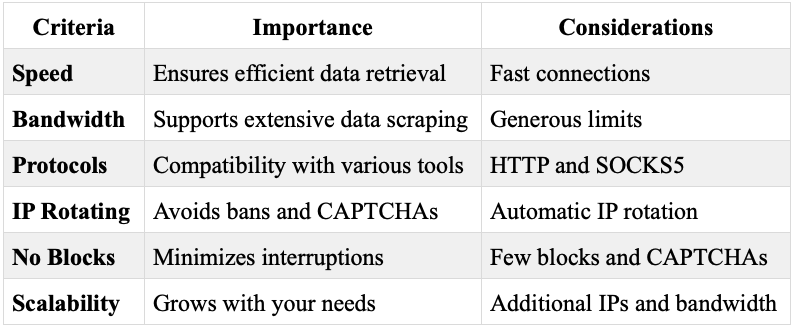
What to Look for When Searching for a Residential Proxy Provider
When selecting a residential proxy provider, consider the following criteria:
Speed
High-speed connections are crucial for efficient data retrieval. Ensure the provider offers fast and reliable connections to handle your data scraping needs.
Traffic/Bandwidth
Look for providers offering generous bandwidth and traffic limits to support extensive data scraping without throttling or additional costs.
Type: HTTP/SOCKS5
Choose a provider that supports both HTTP and SOCKS5 protocols to accommodate various use cases and ensure compatibility with your scraping tools.
IP Rotating
IP rotation helps avoid bans and CAPTCHAs by changing the IP address with each request. Ensure the provider offers automatic IP rotation.
No Blocks or CAPTCHAs
Select a provider known for minimizing IP blocks and CAPTCHAs, ensuring uninterrupted data scraping.
Scalability
Your proxy provider should be able to scale with your needs, offering additional IPs and bandwidth as your data scraping requirements grow.
Table: Criteria for Selecting a Proxy Provider
Drawbacks to Datacenter Proxies
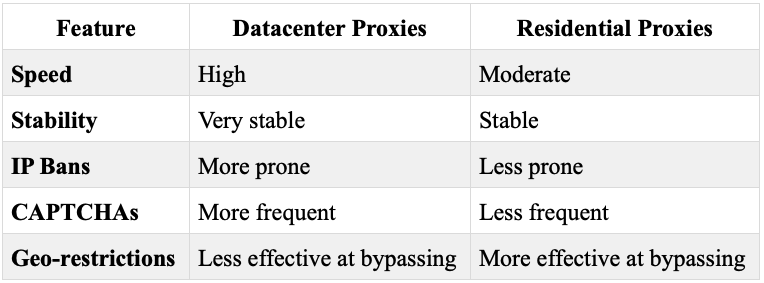
While datacenter proxies offer speed and stability, they have some limitations compared to residential proxies.
Speed and Stability vs. IP Bans and CAPTCHAs
Datacenter proxies excel in speed and stability but are more prone to IP bans and CAPTCHAs. Residential proxies, though slower, are better at handling these challenges and can bypass geo-restrictions more effectively.
Potential Blocks
Since datacenter proxies come from data centers, they are easier for websites to identify and block. This can lead to frequent IP bans and CAPTCHAs, interrupting your data scraping activities.
Table: Comparison of Datacenter and Residential Proxies
Why to Avoid Free Datacenter Proxies
Free datacenter proxies come with several disadvantages:
- Shared IPs: Free proxies are often shared among many users, leading to slow speeds and higher risk of bans.
- High Latency: Shared resources result in higher latency, making them unsuitable for time-sensitive tasks.
- Unreliable Performance: Free proxies lack the reliability and support of paid services, often leading to frequent downtimes and inconsistent performance.
Conclusion: Key Takeaways
When considering datacenter proxies for your data-related tasks, keep the following points in mind:
- Speed and Stability: Datacenter proxies offer high-speed and stable connections.
- Use Cases: Ideal for SERP data scraping, website analysis, and market research.
- Criteria for Providers: Look for speed, bandwidth, HTTP/SOCKS5 support, IP rotating, and scalability.
- Challenges: Be aware of potential IP bans and CAPTCHAs.
- Avoid Free Proxies: Due to shared IPs, high latency, and unreliable performance.
Datacenter proxies are powerful tools for data scraping and analysis, but choosing the right provider and understanding their limitations is crucial for success.


